Herpes affects young adults and usually does not cause any symptoms. Sometimes the symptoms are mild and are mistaken for another skin condition. If you think you have herpes, see your doctor as soon as possible. It’s easier to diagnose when there are sores. You can start treatment sooner and perhaps have less pain with the infection.
What is Genital Herpes?
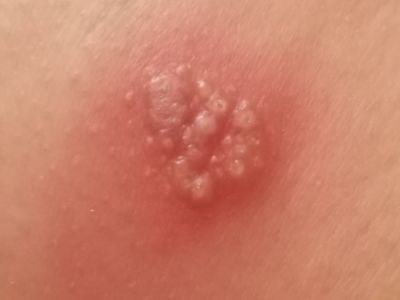
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It causes herpetic sores, which are painful blisters that can break open and ooze fluid.
Sores appear where the infection enters the body. You can spread the infection by touching a sore and then rubbing or scratching another area of your body. Sore usually can develop on or in the:
- Anus
- Mouth
- Urethra
- Vulva
- Buttocks
- Thighs
- Rectum
- Vagina
- Penis
- Scrotum
- Cervix
A higher risk of getting herpes is linked to:
- Contact with genitals through oral, vaginal, or anal sex. Having sexual contact without using a barrier increases your risk of herpes. Barriers include condoms and condom-like protectors called dental dams used during oral sex. Women are at higher risk of getting genital herpes.
- Having sex with multiple partners. The number of people you have sex with is a strong risk factor. Contact with genitals through sex or sexual activity puts you at higher risk.
- Having a partner who has the disease but is not taking medicine to treat it. There is no cure for genital herpes, but medication can help limit outbreaks.
- Certain groups within the population. Women, people with a history of sexually transmitted diseases, older people, Black people in the United States, and men who have sex with men diagnosed with genital herpes at a higher than average rate. People in groups at higher risk may choose to talk to a healthcare provider about their risk.
What Are The Symptoms Of Genital Herpes?
Most people infected with the infection don’t know they have it. They may have no symptoms or very mild symptoms. Symptoms may start about 2 to 12 days after exposure to the virus. They may include:
- Pain or itching around the genitals
- Small bumps or blisters around the genitals, anus, or mouth
- Painful ulcers form when blisters rupture and ooze or bleed
- Scabs that form as the ulcers heal
- Painful urination
- Discharge from the urethra, the tube that releases urine from the body
- Discharge from the vagina
During the first outbreak, you may commonly have flu-like symptoms such as:
- Fever
- Headache
- Body aches
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin
How Does It Affect Young Adults?
Herpes spreads through close contact with a person who has the infection. The virus can be found in the skin and saliva. If you have herpes simplex, you are most likely to pass the virus to another person when you have sores. But you can infect someone else even if you have no symptoms. Healthcare providers call this asymptomatic viral shedding.

People may get HSV-1 through:
- Kissing
- Touching a person’s skin near the mouth
- Sharing food utensils, lip balm, or razors
If you receive oral sex from someone who has a cold sore, it may spread a herpes infection to your genitals.
People may get HSV-2 through:
- Touching open sores, including while breastfeeding
- Childbirth by a mother or gestational parent who has an active infection
- Intercourse, including anal, vaginal-penile and vaginal-vaginal
- Oral sex with someone infected
- Skin-to-skin contact without ejaculation
You can’t get genital herpes from objects like toilet seats. But you could pass genital herpes through shared sex toys.
Some people have few to no herpes outbreaks and choose not to have treatment. But many people prefer to use medications that shorten outbreaks and reduce symptoms.
During an outbreak, you may use an antiviral ointment or cream to help lessen your symptoms and help them go away faster, but it only works if you start it soon after you start an outbreak. Many people with HSV-2 take daily oral medications to keep outbreaks at bay.
To prevent developing herpes, you can use this medication:
- Acyclovir – this drug has antiviral medicine content. It is used for the treatment of illnesses caused by the Herpes Virus. It works by preventing viral DNA fusion and reproduction by inhibiting the DNA polymerase enzyme.