Brain tumor is a mass or growth of abnormal cells in your brain. Many different types of brain tumors exist. Some brain tumors are benign, and some brain tumors are malignant.
Brain tumors can begin in your brain and, other cancer can start in other parts of your body. Brain tumors can affect the function and press the surrounding nerves, tissue, and blood vessel.

Symptoms of Brain Tumor
- Onset or change in the pattern of headaches
- Headaches that gradually become more frequent and more severe
- Vision problems
- Unexplained nausea or vomiting
- Difficulty in balancing
- Speech difficulties
- Tiredness
- Confusion
- Trouble in making decisions
- Gradual loss of sensation or movement in an arm or a leg
- Inability to follow simple rules
- Personality or behavior changes
- Seizures and hearing problems
Brain tumor headaches are adverse to typical migraines. Brain tumor-related headaches are persistent and lead to sharp and stabbing pain.
Types of Brain Tumors
- Gliomas. The tumors start in the glial cells and are often cancerous. Glioblastoma is the most aggressive type of glial tumor.
- Meningiomas. It forms in the thin layer of tissue that covers the brain and spinal cord. Meningiomas are not cancerous but, it causes problems by pressing on your brain.
- Schwannomas. It damages the protective coating of nerve cells. They are benign but may lead to hearing loss and problems in balancing.
- Pituitary adenomas. It sits at the base of your brain and, they are slow-growing. These are benign types of tumors.
Causes and Risk Factors of Brain Tumor
- Family history and age
- Race
- Chemical exposure
- Exposure to radiation
- No history of chickenpox
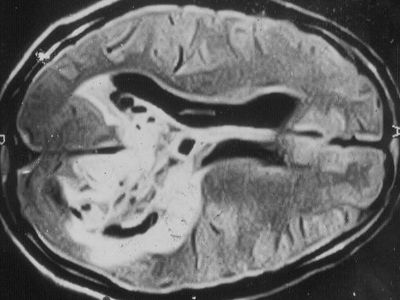
Stages of Brain Tumor
Tumor histology includes finding out the type of tumor and grade. For most tumors, the lower the grade level, the better the prognosis. Stages/Grade of brain tumor:
Grade 1. It is noncancerous and resembles healthy cells in appearance. It is often treatable with surgery.
Grade 2. The tumors are malignant but slow-growing. These tumors can spread to adjacent tissues or recur after initial therapy.
Grade 3. It is malignant and develops more quickly than grade 1 and 2 tumors. Under the microscope, the malignant cells display severe abnormalities. It can generate abnormal cells that can spread to areas of the brain.
Grade 4. The brain tumors develop rapidly and have various abnormal features under a microscope. The timeline of the growth of the cancer cell is aggressive.
How to Diagnose Brain Tumor?
- Diagnosis of a brain tumor begins with a physical exam and a look at your medical history.
- CT scan of the head
- MRI of the head
- Angiography
- Skull X-rays
- Biopsy
Treatment for Brain Tumor
Treatment includes Anti-cancer medications upon diagnosis. Other treatment method includes:
- Brain surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy