Seborrheic dermatitis causes scaly patches, inflamed skin, and stubborn dandruff. This condition can be irritating, but it’s not contagious and doesn’t cause permanent hair loss. This condition may go away without treatment, or you may need to use medicated shampoo or other products long-term to clear up symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
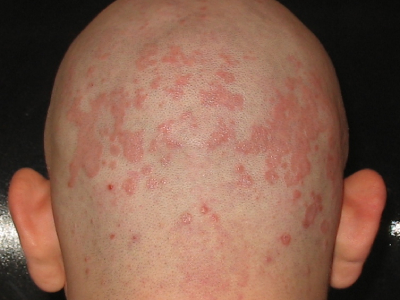
This is a very common skin disease that causes a rash. When this rash appears, it often looks like the one shown on this page. The skin tends to have a:
- Reddish color
- Swollen and greasy appearance
- White or yellowish crusty scale on the surface
- One or more of these rashes can appear on the body. Sometimes, the affected skin itches.
See your health care provider if:
- You’ve tried self-care steps, but your symptoms persist.
- You’re so uncomfortable that you’re losing sleep or are distracted from your daily routines.
- You think your skin is infected.
- Your condition makes you feel embarrassed or anxious.
Risk factors for seborrheic dermatitis include:
- Stress
- Fatigue
- A change of season
- Nervous system conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease
- Having a mental health condition, such as depression
- Immune system disorders, such as HIV infection
- Recovery from stressful medical conditions, such as a heart attack
What Is The Cause Of Seborrheic Dermatitis?
A combination of genetic and environmental factors usually causes seborrheic dermatitis. The trigger is usually an inflammatory reaction to excess Malassezia yeast, sometimes called pityrosporum. This organism which normally lives on the skin’s surface, is the likely cause of seborrheic dermatitis. The Malassezia overgrows, and the immune system seems to overreact to it, leading to a fungal infection that results in skin changes.
Certain medical conditions can increase people’s risk of developing seborrheic dermatitis, including psoriasis, acne, HIV, rosacea, Parkinson’s disease, alcoholism, epilepsy, depression, eating disorders, and recovery from a stroke or heart attack.
Common triggers for seborrheic dermatitis include:
- Stress
- Harsh detergents, solvents, chemicals, and soaps
- Recoveries from a stressful life event, like losing a loved one or a heart attack
- Hormonal changes or illness
- Cold, dry weather or a change in the season
- Some medications, including psoralen, interferon, and lithium
- Certain medical conditions, such as HIV and Parkinson’s disease
Like all forms of eczema, seborrheic dermatitis is not contagious. You cannot catch it from another person. Instead, it’s the result of environmental and genetic factors.
What Are The Treatment For Seborrheic Dermatitis?
The main treatments for seborrheic dermatitis for adolescents and adults are medicated shampoos, creams, and lotions. If non-prescription products and self-care habits don’t help, your healthcare provider might suggest that you try one or more of these treatments:
- Antifungal gels, creams, lotions, foams, or shampoos alternated with another medication.
- Creams, lotions, shampoos, or ointments that control inflammation.
- The antifungal medication you take as a pill.
Recommended medication that can be used for the condition:
- Permethrin – is a topical preparation used to treat an infection. This medicine works by paralyzing and killing the parasites in your body. It also works by interfering with the protein synthesis of the parasite. It destroys the cell wall that is necessary for their survival. It kills the parasite and its eggs. The remaining bacteria will also die.
The following non-prescription treatments and self-care tips may help you:
- Soften and remove scales from your hair. Apply mineral oil, peanut oil, or olive oil to your scalp.
- Wash your skin regularly. Use warm, not hot, water and a gentle soap or non-soap cleanser.
- Apply a medicated cream. If that doesn’t work, try the antifungal cream ketoconazole.
- Don’t use styling products.
- Don’t use skin and hair products that contain alcohol. These can cause the disease to flare up.
- If you have a beard or mustache, shampoo facial hair regularly. Seborrheic dermatitis can be worse under mustaches and beards.
- Gently clean your eyelids. If your eyelids are inflamed or scaly, wash them each night. Warm, damp cloths pressed to your eyelids also may help.
- Gently wash your baby’s scalp. If your infant has a mild cradle cap, wash the scalp with a mild baby shampoo once a day. If scaling persists, apply mineral or olive oil to the scalp for an hour or two.