GERD is chronic acid reflux. It occurs when acid-containing contents from your stomach leak back into your esophagus, the tube leading from your throat to your stomach. The lower esophageal sphincter does not close properly when food reaches the stomach, causing acid reflux. A sour taste results from acid backwashing back up through your esophagus, throat, and mouth.

What are the Symptoms of GERD?
- Persistent heartburn
- Acid regurgitation
- Chest pain
- Horseness in the morning
- Trouble swallowing or throat tightness
- Bad breath
- Dry cough
In severe cases of GERD, symptoms can include:
- Black or bloody stool
- Weight loss
- Vomiting
- Pain in the mid and upper abdomen
Fortunately, acid-related heartburn has treatment and they are also manageable. Your doctor can also provide medications to reduce stomach acid.
Risk Factors of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Large meals
- Fried and fatty foods
- NSAIDs
- Tea and coffee
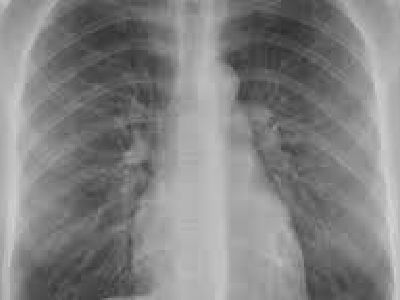
How to Diagnose Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)?
- X-ray of your upper GI tract shows any problems related to GERD.
- Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and biopsy.
- CT Scan
- Esophageal pH and impedance monitoring to measure the pH levels of your esophagus.
- Health assessment is done by medical providers
- Stool and urine test
- Esophageal manometry to measure the strength of your sphincter, muscles, and spasms as you swallow.
Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Treating GERD includes acid reducers, proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, and other recommended treatments from your medical provider. Acid reducer medicines offer quick treatment of heartburn and stomach acid. Follow the recommendations from your doctor to prevent it from worsening.
Quit smoking and maintain a healthy diet to balance the stomach acids and prevent heartburn. Avoid certain drinking and eating habits. Avoid the typical trigger and finish the treatment with proper medications.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Diet Tips
Acids are present in the stomach but can escape in the throat during acid reflux. It results in chest pain and heartburn. Follow a proper diet to manage the symptoms.
- Avoid large meals because it can put pressure on the stomach. Avoid sitting down or slouching after eating as it puts pressure on the stomach.
- Avoid eating foods 3 hours before bedtime as it is more likely to cause stomach acid release.
- Eat slowly and choose fiber-rich foods.

Here are food and drinks to avoid as part of the preventive Measures of GERD:
- High-fat foods
- Spicy foods
- Chocolates
- Peppermints
- Onions
- Citrus fruits and juices
- Tomato sauce
- Alcoholic beverages
- Carbonated drinks
- Coffee