The athlete’s foot is a fungal infection that begins between the toes. It occurs in people having sweaty feet while using tight-fitting shoes. Athletes’ foot is closely related to fungal infections such as ringworm and jock itch. It is highly treatable with proper medications.
Is Athlete’s Foot Contagious?
It is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. It can also spread to the toenails and the hands. Athletes’ foot is not life-threatening but they are hard to cure. A weakened immune system and diabetes can worsen the condition.
Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot
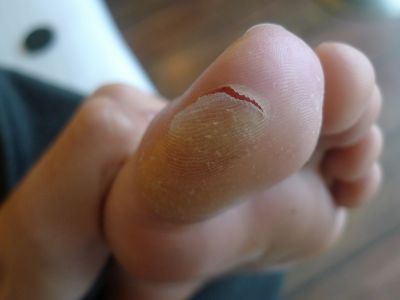
- Scaly, peeling and cracking of skin between the toes
- Itchiness after taking off your shoes and socks
- Inflamed skin
- Reddish or purplish of your skin color
- Burning or stinging
- Blisters
- Dry and scaly skin on the bottom of the foot that extends up the side
What Causes Athlete’s Foot?
The athlete’s foot occurs when the Tinea fungus grows on the feet. It spreads through direct contact with an infected person, or by touching surfaces contaminated with the fungus. The fungus thrives in warm, moist environments. It is frequent in showers, on locker room floors, and around swimming pools.
What are the Risk Factors of Athlete’s Foot?

- Walking barefoot in public places, locker rooms, swimming pools, and showers.
- Sharing socks, towels, and shoes with an infected person
- Wearing tight socks and shoes in a lengthier period
- Sweaty feet
- Minor skin and nail injury of the foot
Complications of Athlete’s Foot
Mild complications of the athlete’s foot include an allergic reaction to the fungus. It causes blistering on the feet or hands and it can possibly return after treatment. Severe complications if a secondary bacterial infection develops and causes swelling, and pain in the affected area. Pus, drainage, and fever are additional signs of a bacterial infection.
How to Diagnose Athlete’s Foot?
Your doctor will assess your symptoms and recommends a skin test to determine the causes of the infection. Athletes’ feet can normally be diagnosed by observing the hallmark signs.
A skin lesion potassium hydroxide exam is the most common test for an athlete’s foot. A doctor scrapes off a small area of infected skin and places it in potassium hydroxide. It destroys normal cells and leaves the fungal cells untouched so they are easy to see under a microscope.
Treatment for Athlete’s Foot
For mild infections, your doctor may recommend antifungal medications. Over-the-counter medications and topical treatments are also available.