Antifungal drugs treat fungal infections. Fungus in the soil, air, and on your skin can cause yeast infections, ringworm, and nail and skin infections. Breathing in fungal spores can lead to respiratory illnesses. People with weak immune systems are more prone to fungal infections requiring antifungal medicine.
What are Antifungal Drugs?
Antifungals are medicines that kill or stop the growth of fungi that cause infections. They are also called antimycotic agents. There are OTC and prescription antifungal medications. Talk to your healthcare provider about what treatment to use.
Antifungals come in different forms, including:
- Injections (shots) or IV
- Oral pills or liquids
- Topical (skin) creams, ointments, gels, and sprays
- Vaginal suppositories
Fungal infections can affect the following:
- Circulatory system
- Respiratory system
- Skin and nails
Fungi grow as yeasts, molds, or a combination of both. They reproduce through very tiny spores. These spores can exist in soil or become airborne. You can also have naturally occurring fungi, like Candida yeast, in your body. Fungi live on your skin, inside your digestive system and vagina.
Anyone can get a fungal infection. Most fungi cause no problems, and the infections are easily treatable. People with compromised immune systems are more likely to develop serious fungal infections. These infections are called opportunistic infections. They can be life-threatening for people who have:
- AIDS
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus
- Cancer
- Organ transplants
- Stem cell transplants
High-recommended antifungal medication:
- Permethrin – belongs to the Pyrethrin group of drugs. This medicine works by paralyzing and killing the parasites in your body. It also works by interfering with the protein synthesis of the parasite. It destroys the cell wall that is necessary for their survival. It kills the parasite and its eggs. The remaining bacteria will also die. The infection will not invade your body, and the rest of you will be treated.
What Are Its Uses?
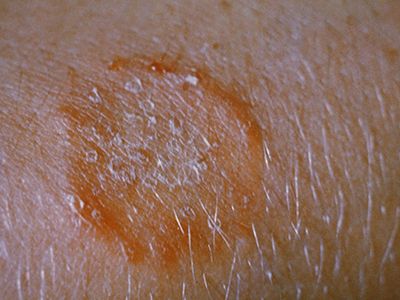
Fungal infections commonly treated with antifungals include:
- Ringworm
- Athlete’s foot
- Fungal nail infection
- Vaginal thrush
- Some types of severe dandruff
Some fungal infections can grow inside the body and must be treated in the hospital.
- Examples include:
- Aspergillosis, which affects the lungs
- Fungal meningitis, which affects the brain
You are more at risk of getting one of these more serious fungal infections if you have a weakened immune system – for instance, taking medicines to suppress your immune system.
Antifungal resistance means a fungus no longer responds to treatment. This response makes the fungal infection harder to treat. Some fungi are naturally resistant to certain antifungals. Fungi may also develop resistance when you use antifungal medicine for a long time. Skipping doses, stopping treatment too soon, or receiving too little can also lead to antifungal resistance.
What Are Its Side Effects?
Before using any antifungal medicine, speak to a pharmacist or doctor about the following:
- Any other medications you’re using because they may cause problems when used with antifungals
- If you have any medical conditions or allergies
- If antifungals can be used if you’re pregnant or breastfeeding
- The possible side effects of the antifungal medication
Antifungals usually don’t cause side effects, but they tend to be mild and short-lived if they do. These side effects may include:
- Itching or burning
- Redness
- A rash
- Tummy pain
- Diarrhoea
- Headache
- Feeling sick (nausea)
- Being sick (vomiting)
You can check the information leaflet with your medication if you want a complete list of possible side effects and cautions. Sometimes, but not often, oral antifungal medications can cause serious side effects, usually when used for a long time. Oral antifungals used for nail infections, for instance, can lead to rare but severe side effects, such as liver damage, which is why a doctor may do a blood test before you start taking this medicine and a few weeks after you start taking it to monitor its effects. Each antifungal has its side effects, so discuss these with a doctor before starting the medicine.